Explain Critical Section Problem With Its Different Solutions
Swap Solution to the Critical Section Problem. The following problems of synchronization are considered as classical problems.
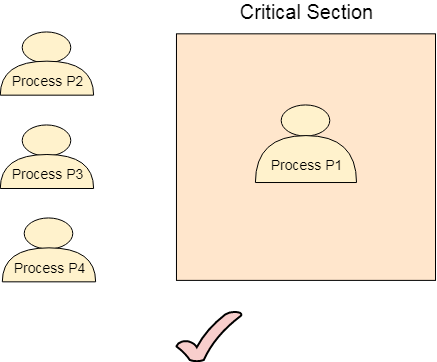
Os Critical Section Problem Javatpoint
Process Critical Section releaseLock.
. Solutions To The Critical Section Peterson Solution. Our solution must provide mutual exclusion. If process Pi is executing in its critical section then no other processes can be executing in their critical sections.
When a thread is executing in its critical section no other threads can be executing in their critical sections. Pn-1 Every process has critical section segment of code. If a process A is executing in its critical section then no other processes must execute in its critical section.
Operating System Windows MCA. Solution to Implement Critical Section. Consider system of n processes p0 p1.
First the program has to execute the code written in entry section and if it clears then only it can execute the code of the critical section. If no process is currently in its critical section then. Requirements of Synchronization mechanisms Primary.
If lock is false then a process can enter the critical section and otherwise it cant initially lock is false repeat. Critical section lock false. In Binary Semaphore only two processes can compete to enter into its CRITICAL SECTION at any point in time apart from this the condition of mutual exclusion is also preserved.
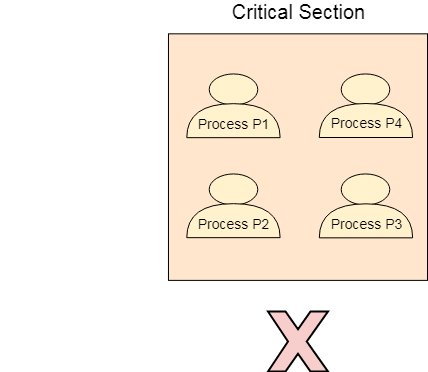
We need to provide a solution in such a way that the following conditions can be satisfied. Mutual exclusion implies that only one process can be inside the critical section at any time. One way to do that is by writing a entry section in both the programs.
A critical section is a region of code in which a process uses a variable which may be an object or some other data structure that is shared with another process eg. These are summarized for detailed explanation you can view the linked articles for each. The lock can be acquired by only one thread.
Mutual exclusion only one process can enter critical section at a time Progress a process not wishing to enter its critical section should not block a process whishing to enter its critical section. A solution to critical section problem must satisfy the following requirements. By Mutual Exclusion we mean that if one process is executing.
Petersons solution is widely used solution to critical section problems. Explain necessarr and sufficient condition for deadlock 10 to occur. Formal Definition of Critical Sections The overlapping portion of each process where the shared variables are being accessed.
Critical section. Both busy waiting and blocking methods can be used as means to address critical section problems and process. Sections then one of these threads will get into the critical section.
A simple solution to the critical section can be thought as shown below acquireLock. A solution to a critical section problem must satisfy three conditions. Uses two variables called lock and key.
Every critical section must end with an exit condition which alerts the system regarding the exit. If no process is executing in its critical section and some processes wish to enter their critical sections. What is deadlock.
A thread must acquire a lock prior to executing a critical section. Bounded-buffer or Producer-Consumer Problem 2. The Critical Section Problem Concurrent Software Systems 2 Problem Description Informally a critical section is a code segment that accesses shared variables and has to be executed as an atomic action.
A solution to a critical section problem must satisfy three conditions. A solution to the critical-section problem must satisfy the following three requirements. Explain Linux OS with respect to Kernel memory management and 10 10 10 10 b b scheduling.
If a process A is executing in its critical section then no other processes must execute in its critical section. To avoid this problem race condition we have to synchronize both programs. There can be many solutions to implement critical section but as we studied above the solution must satisfy three criteria ie.
Typically critical sections prevent thread and process migration between processors and the preemption of processes and threads by interrupts and other processes and threads. The critical section problem refers to the problem of how to ensure that at most one process is executing its critical section at a given time. If no thread is executing in its critical section and if there are some threads that wish to enter their critical sections then one of these threads will.
If no process is currently in its critical section then. If any other processes require the critical section they must wait until it is. There are various ways to implement locks in the above pseudo code.
The critical section problem refers to the problem of how to ensure that at most one process is executing its critical section at a given time. The solution to the critical section problem must satisfy the following conditions. Petersons solution provides a good algorithmic description of solving the critical-section problem and illustrates some of the complexities involved in designing software that addresses the requirements of mutual exclusion progress and bounded waiting.
Every critical section must end with an exit condition which alerts the system regarding the exit. Explain different file access methods Explain critical section problem with its derent solutions. Critical sections often allow nesting.
Explain deadlock avoidawe prevention and detection. Critical sections in different threads are not necessarily the same code segment. Section 2 unlock the process when you are done executing the critical section and 3 wait to use the critical section of code if it is already locked 4 never have to wait forever when trying to get to your critical section.
While flagj. The problem we have just illustrated is called the critical section problem. 130 views Related Answer.
Some times the problems of the Critical Section are also resolved by hardware. In order to synchronize the cooperative processes our main task is to solve the critical section problem. Process may be changing common variables writing.
Mutual Exclusion --- if is executing in one of its critical sections no is executing in its critical sections. And if one program has cleared the entry section code. Readers and Writers Problem 4.
Do flagi true. Necessary and sufficient conditions for a solution to the cs. The critical section problem needs a solution to synchronize the different processes.
The code that read modified and wrote an account balance in the example you did. Let us discuss them in future articles. To solve the problem occurred above of race condition we are going to use Binary Semaphore and Counting Semaphore.
Critical Section Problem A piece of code inside a process that wants access to shared resources and that need not be executed while another process is in a corresponding section of code. Var true while var true swaplock var.

Critical Section Problem System Solutions Process

Comments
Post a Comment